Model-based RL is a promising approach for real-world robotics due to its improved sample efficiency and generalization capabilities compared to model-free RL. However, effective model-based RL solutions for vision-based real-world applications require bridging the sim-to-real gap for any world model learnt. Due to its significant computational cost, standard domain randomisation does not provide an effective solution to this problem. This paper proposes TWIST (Teacher-Student World Model Distillation for Sim-to-Real Transfer) to achieve efficient sim-to-real transfer of vision-based model-based RL using distillation. Specifically, TWIST leverages state observations as readily accessible, privileged information commonly garnered from a simulator to significantly accelerate sim-to-real transfer. Specifically, a teacher world model is trained efficiently on state information. At the same time, a matching dataset is collected of domain-randomised image observations. The teacher world model then supervises a student world model that takes the domain-randomised image observations as input. By distilling the learned latent dynamics model from the teacher to the student model, TWIST achieves efficient and effective sim-to-real transfer for vision-based model-based RL tasks. Experiments in simulated and real robotics tasks demonstrate that our approach outperforms naive domain randomisation and model-free methods in terms of sample efficiency and task performance of sim-to-real transfer.
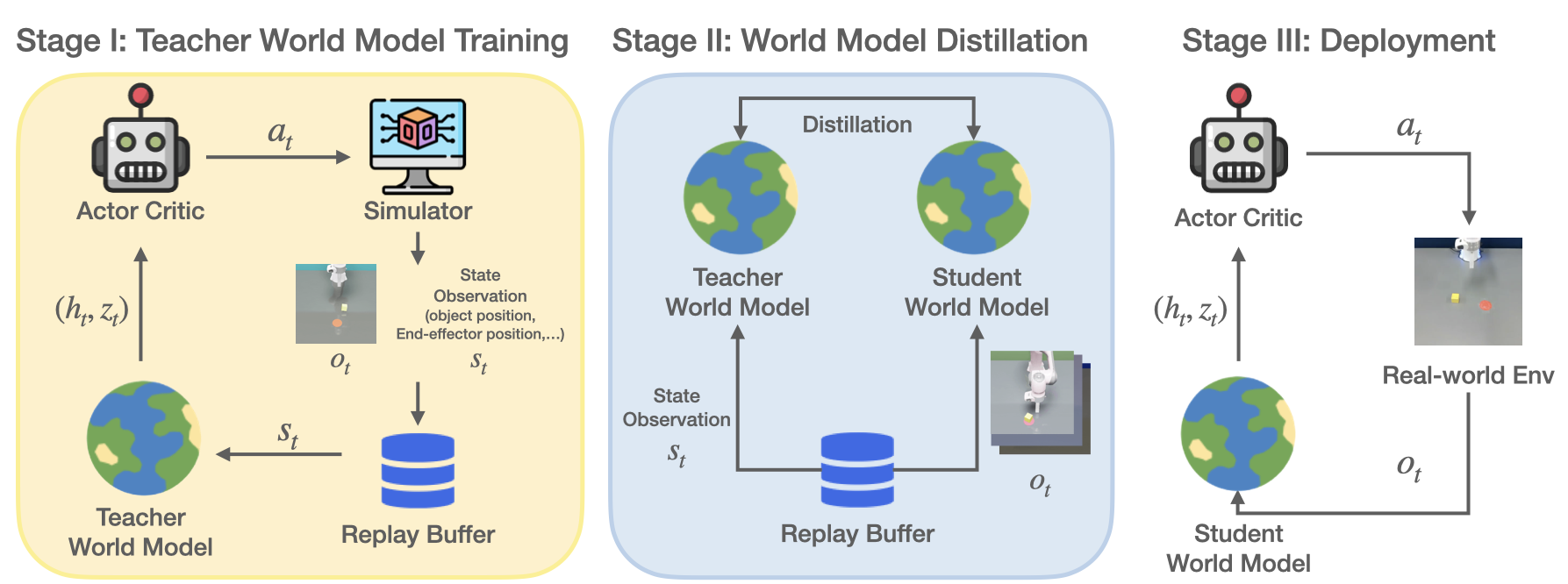
Our approach consists of three stages. Firstly, a teacher world model and its associated policy are trained from state observations, which are easily accessible privileged information in simulation. While training the teacher, a matching dataset of domain-randomized image observations is generated. Next, by leveraging the collected state and domain-randomized image observations, the teacher supervises a student world model by imitating the latent states of the world models. In particular, the student imitates the deterministic representation, prior, and posterior distribution of the teacher world model. Finally, we transfer the student world model and the policy to a real-world environment. The student world model encodes the current image observation to latent representation with aggregation of previous latent states, and that is used as input to the policy for execution.

To better match the representations between the student and teacher world model, we further derive a training signal for distribution alignment by matching imagined rollouts in both the teacher and student models. Firstly, an imagined trajectory is generated using the learned policy with the teacher model. We also collect an imagined trajectory in the student model by replaying the same sequence of actions used for trajectory imagination in the teacher. Then, we align the deterministic representation and prior distribution in the trajectories generated by the teacher and student.
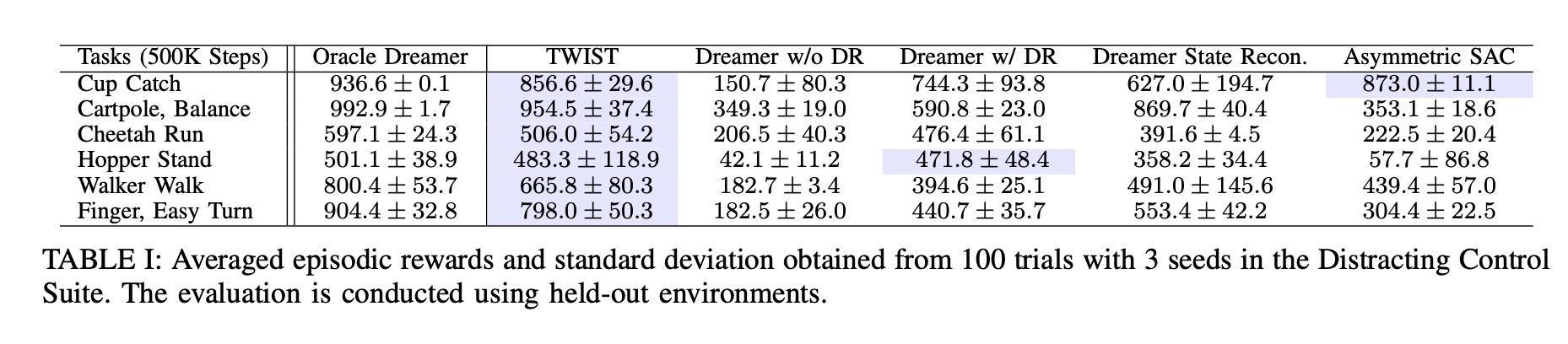
Our preliminary experiments conducted in DMControl suite show that TWIST outperforms baseline methods including Dreamer with naive domain randomization and model-free RL in both sim-to-sim and sim-to-real experiments by a significant margin.
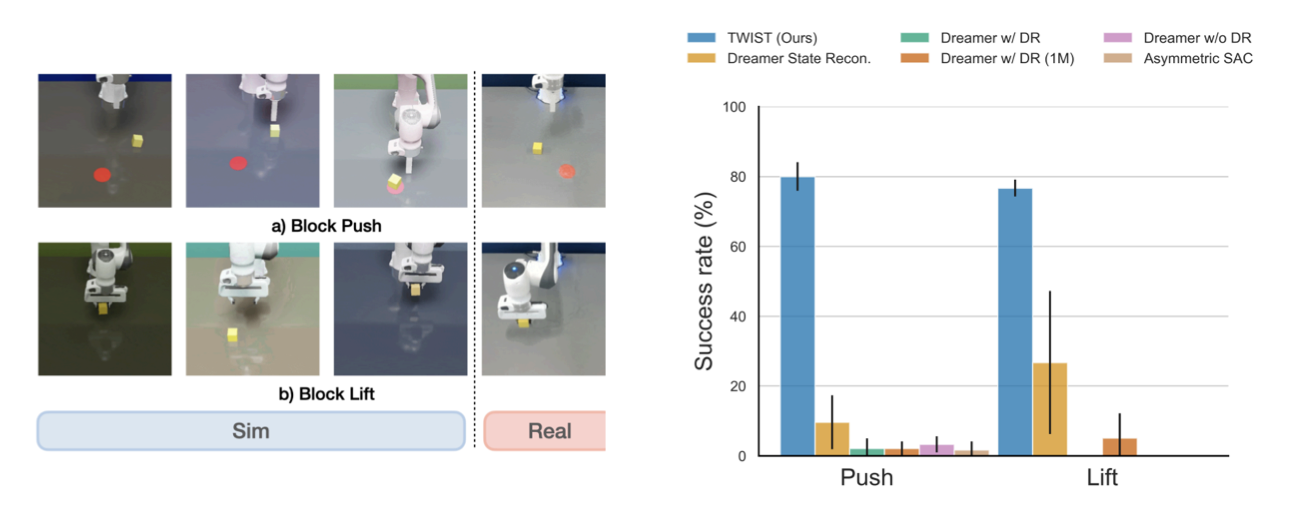
In our real-world experiments, we demonstrate that TWIST is capable of solving manipulation tasks in the real world with improved sample efficiency. On the other hand, baseline methods struggle to learn a policy efficiently with a limited amount of samples in simulation, thus these methods often fail to solve the task in the real world.
TWIST (Our method)
Dreamer State Recon.
Dreamer w/ DR
Asymmetric SAC
TWIST (Our method)
Dreamer State Recon.
Dreamer w/ DR
Asymmetric SAC
@article{yamada2023twist,
title={TWIST: Teacher-Student World Model Distillation for Efficient Sim-to-Real Transfer},
author={Yamada, Jun and Rigter, Marc and Collins, Jack and Posner, Ingmar},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2311.03622},
year={2023}
}